HOME > Publication & Reports > Annual Report 2016 > Exploratory Oncology Research & Clinical Trial Center
Division of Cancer Immunology
Hiroyoshi Nishikawa, Chika Sakai, Eri Sugiyama, Yasuko Tada, Yosuke Togashi, Shodai Fukuoka, Konomi Onagawa, Tomoka Takaku, Yoshiko Takeuchi, Megumi Takemura, Miyuki Nakai, Yuki Fujioka, Tomomi Yamazaki, Sayuri Yoshimatsu, Sho Isoyama, Sayoko Shinya, Masahiro, Tokunaga, Takahiro Negishi, Hiroki Fukutomi, Motoya Mie, Hisashi Yoshimi
Introduction
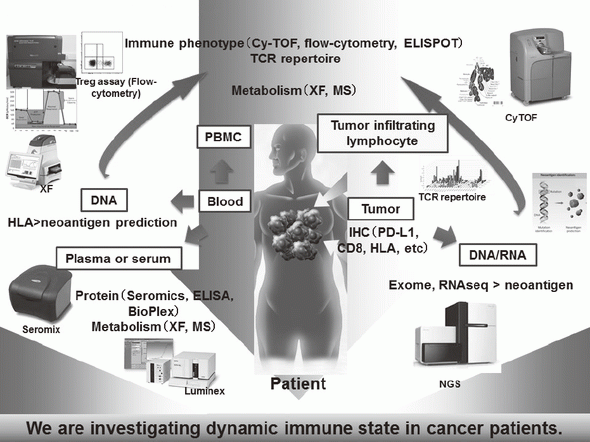
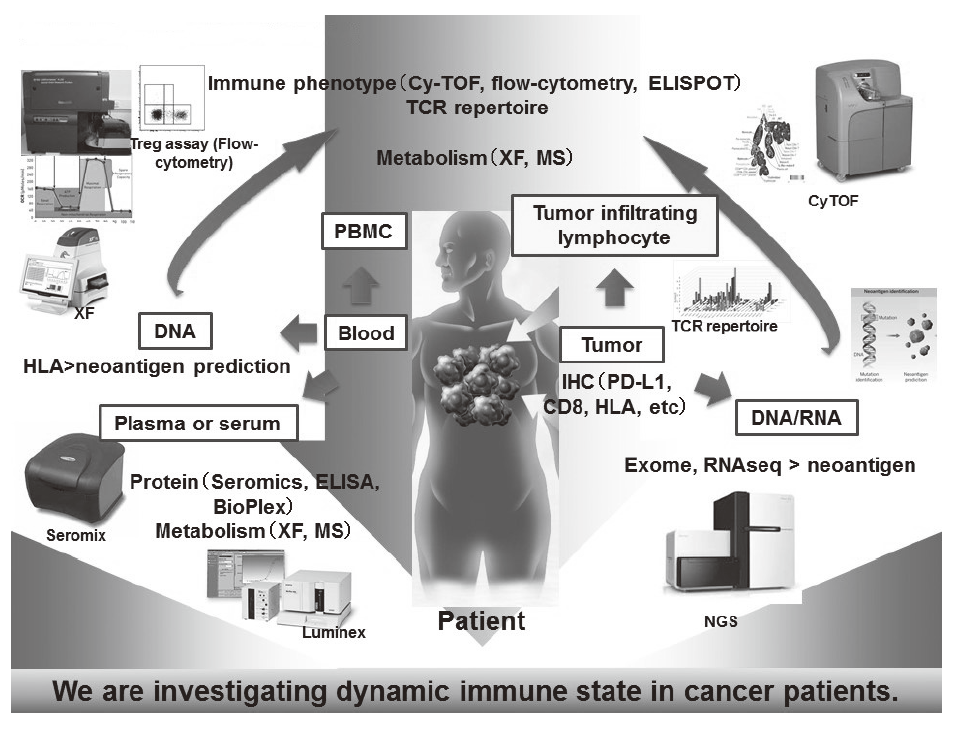
Recent success of cancer immunotherapy, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors, makes a key strategy for cancer treatment and a lot of clinical trials are under investigation for developing new reagents. Among patients receiving cancer immunotherapy, more than half of the patients fail to exhibit clinical benefits even though some do experience long-lasting clinical benefits. Moreover, patients sometimes experience immune-related adverse effects, such as thyroiditis and hypophysitis without any clinical benefits. It is therefore urgently required to identify biomarkers that can discern responders from non-responders in the cancer immunotherapy field. To accomplish this, variable immune cells in both tumor microenvironments, and peripheral blood are investigated in our division (Figure 1).
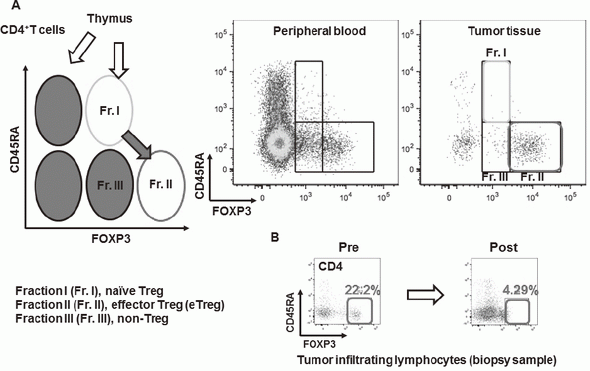
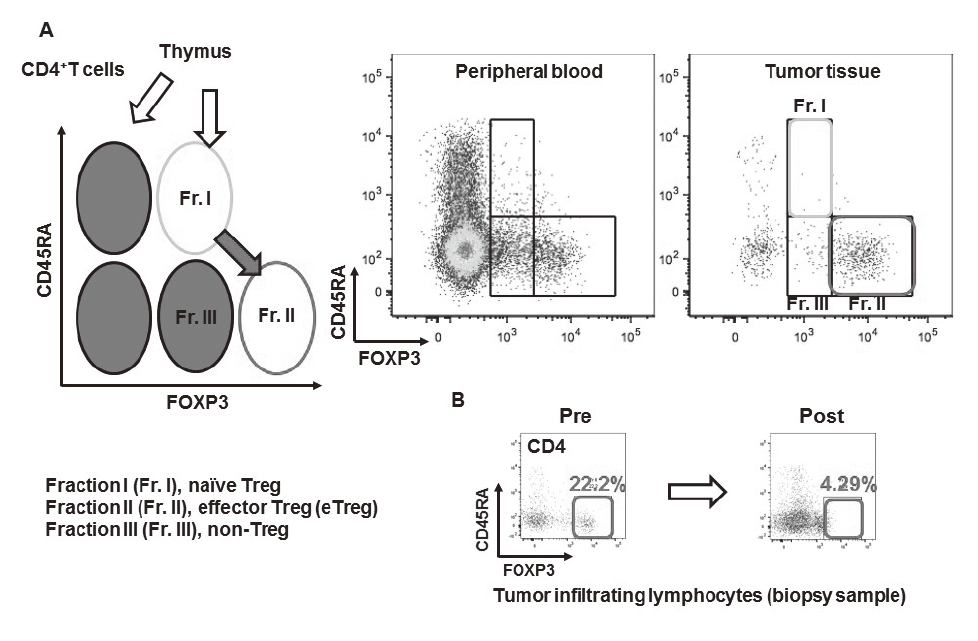
Especially, regulatory T cells (Tregs), which have a suppressive function and are known to be a critical component to inhibit anti-tumor immunity, are analyzed using our original assay (effector Tregs; eTregs) (Figure 2A). Furthermore, with the findings from clinical samples analyses, we also reverse-translate into basic researches to elucidate the essential mechanisms of immune responses to cancer.
Research activities
Various cancers have been classified into subgroups based on genomic alterations; meanwhile, classification by genomic alterations shows limitations to elucidate detailed immune status in tumor microenvironment due to the complexity of the immune system. When the data from our assays of tumor microenvironment immune status were integrated with genomic analyses in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), significant differences between EGFR-mutated and wild-type NSCLC were identified (submission prepared). In addition, we have found an immunological marker expressed by T cells related to somatic mutation burden, one candidate for the efficacy of immunotherapy (submission prepared).
A real-time immune monitoring system in cancer patients during their cancer treatment has been established by collaboration with many clinical divisions showing that there were significant differences in the immune state changes of tumor microenvironment among chemotherapies including not only immune checkpoint inhibitors, but also cytotoxic reagents. We also found a reduction of eTregs by a first-in-human clinical reagent using this system, proposing a novel effect of this drug (Figure 2B).
Education
Two graduate students are trained in our division, and five new students will join in the next year. After finishing their thesis, they will continue to study cancer immunology abroad. New post-doctoral fellows will also join, resulting in broadening the research area of cancer immunology. Young residents are also trained in our division to become physician scientists.
Future prospects
We integrate our tumor microenvironment immune state data with genomic alterations in many cancer types resulting in the establishment of "cancer immune genome atlas". Mechanistic studies are also addressed based on these clinical findings.
Our real-time immune monitoring system in cancer patients pre- during and post-cancer treatment is supposed to be attractive to and appreciated from a lot of companies in the effective drug development field. Therefore, many collaborative studies with such companies associated with clinical trials are ongoing and planned, which will become a valuable framework for translational and reverse-translational researches.
List of papers published in 2016
Journal
1.Saito T, Nishikawa H, Wada H, Nagano Y, Sugiyama D, Atarashi K, Maeda Y, Hamaguchi M, Ohkura N, Sato E, Nagase H, Nishimura J, Yamamoto H, Takiguchi S, Tanoue T, Suda W, Morita H, Hattori M, Honda K, Mori M, Doki Y, Sakaguchi S. Two FOXP3+CD4+ T cell subpopulations distinctly control the prognosis of colorectal cancers. Nat Med, 22:679-684, 2016
2.Takeuchi Y, Nishikawa H. Roles of regulatory T cells in cancer immunity. Int Immunol, 28:401-409, 2016
3.Ureshino H, Shindo T, Nishikawa H, Watanabe N, Watanabe E, Satoh N, Kitaura K, Kitamura H, Doi K, Nagase K, Kimura H, Samukawa M, Kusunoki S, Miyahara M, Shin-I T, Suzuki R, Sakaguchi S, Kimura S. Effector Regulatory T Cells Reflect the Equilibrium between Antitumor Immunity and Autoimmunity in Adult T-cell Leukemia. Cancer Immunol Res, 4:644-649, 2016
4.Kakihana K, Fujioka Y, Suda W, Najima Y, Kuwata G, Sasajima S, Mimura I, Morita H, Sugiyama D, Nishikawa H, Hattori M, Hino Y, Ikegawa S, Yamamoto K, Toya T, Doki N, Koizumi K, Honda K, Ohashi K. Fecal microbiota transplantation for patients with steroid-resistant acute graft-versus-host disease of the gut. Blood, 128:2083-2088, 2016
5.Haseda F, Imagawa A, Nishikawa H, Mitsui S, Tsutsumi C, Fujisawa R, Sano H, Murase-Mishiba Y, Terasaki J, Sakaguchi S, Hanafusa T. Antibody to CMRF35-Like Molecule 2, CD300e A Novel Biomarker Detected in Patients with Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes. PLoS One, 11:e0160576, 2016
6.Okubo K, Wada H, Tanaka A, Eguchi H, Hamaguchi M, Tomokuni A, Tomimaru Y, Asaoka T, Hama N, Kawamoto K, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Nagano H, Sakaguchi N, Nishikawa H, Doki Y, Mori M, Sakaguchi S. Identification of Novel and Noninvasive Biomarkers of Acute Cellular Rejection After Liver Transplantation by Protein Microarray. Transplant Direct, 2:e118, 2016
7.Terashima M, Togashi Y, Sato K, Mizuuchi H, Sakai K, Suda K, Nakamura Y, Banno E, Hayashi H, De Velasco MA, Fujita Y, Tomida S, Mitsudomi T, Nishio K. Functional Analyses of Mutations in Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Genes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Double-Edged Sword of DDR2. Clin Cancer Res, 22:3663-3671, 2016
8.Nakamura Y, Togashi Y, Nakahara H, Tomida S, Banno E, Terashima M, Hayashi H, de Velasco MA, Sakai K, Fujita Y, Okegawa T, Nutahara K, Hamada S, Nishio K. Afatinib against Esophageal or Head-and-Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Significance of Activating Oncogenic HER4 Mutations in HNSCC. Mol Cancer Ther, 15:1988-1997, 2016
9.Banno E, Togashi Y, Nakamura Y, Chiba M, Kobayashi Y, Hayashi H, Terashima M, de Velasco MA, Sakai K, Fujita Y, Mitsudomi T, Nishio K. Sensitivities to various epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors of uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutations L861Q and S768I: What is the optimal epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor? Cancer Sci, 107:1134-1140, 2016
10.Hibi M, Kaneda H, Tanizaki J, Sakai K, Togashi Y, Terashima M, De Velasco MA, Fujita Y, Banno E, Nakamura Y, Takeda M, Ito A, Mitsudomi T, Nakagawa K, Okamoto I, Nishio K. FGFR gene alterations in lung squamous cell carcinoma are potential targets for the multikinase inhibitor nintedanib. Cancer Sci, 107:1667-1676, 2016
11.Chiba M, Togashi Y, Tomida S, Mizuuchi H, Nakamura Y, Banno E, Hayashi H, Terashima M, De Velasco MA, Sakai K, Fujita Y, Mitsudomi T, Nishio K. MEK inhibitors against MET-amplified non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol, 49:2236-2244, 2016
12.Tanizaki J, Banno E, Togashi Y, Hayashi H, Sakai K, Takeda M, Kaneda H, Nishio K, Nakagawa K. Case report: Durable response to afatinib in a patient with lung cancer harboring two uncommon mutations of EGFR and a KRAS mutation. Lung Cancer, 101:11-15, 2016
13.Osamura T, Takeuchi Y, Onodera R, Kitamura M, Takahashi Y, Tahara K, Takeuchi H. Characterization of tableting properties measured with a multi-functional compaction instrument for several pharmaceutical excipients and actual tablet formulations. Int J Pharm, 510:195-202, 2016
14.Hayakawa Y, Kawada M, Nishikawa H, Ochiya T, Saya H, Seimiya H, Yao R, Hayashi M, Kai C, Matsuda A, Naoe T, Ohtsu A, Okazaki T, Saji H, Sata M, Sugimura H, Sugiyama Y, Toi M, Irimura T. Report on the use of non-clinical studies in the regulatory evaluation of oncology drugs. Cancer Sci, 107:189-202, 2016
15.Shimazu Y, Hishizawa M, Hamaguchi M, Nagai Y, Sugino N, Fujii S, Kawahara M, Kadowaki N, Nishikawa H, Sakaguchi S, Takaori-Kondo A. Hypomethylation of the Treg-Specific Demethylated Region in FOXP3 Is a Hallmark of the Regulatory T-cell Subtype in Adult T-cell Leukemia. Cancer Immunol Res, 4:136-145, 2016