HOME > Publication & Reports > Annual Report 2016 > Hospital East
Department of Diagnostic Radiology
Masahiko Kusumoto, Ryoko Iwata, Yoshihiro Nakagami, Tatsushi Kobayashi, Kaoru Shimada, Kensuke Inamura, Hayato Tomita, Kotaro Sekiya, Hirofumi Kuno
Introduction
The Department of Diagnostic Radiology is committed to improving health through excellence in image-oriented patient care and research. Our department performs approximately 100,000 inpatient and outpatient procedures annually. Our department also conducts clinical scientific researches as well as basic scientific studies, with the results translated directly into better patient care.
Our team and what we do
Our department has four multi-slice CT scanners including two area detector CT scanners and one Dual Source CT, two 3T MRI systems, one interventional radiology (IR) CT system, one Multi-axis c-arm CT system, two gamma cameras with the capacity for single photon emission CT (SPECT), two digital radiographic (DR) systems for fluoroscopy, two mammographies (MMG), and four computed radiographic (CR) systems. Our IR-CT systems use digital subtraction angiography with multi-detector computerized tomography (MDCT). A positron emission tomography (PET) scanner and a baby cyclotron have been installed, and tumor imaging using 18F-FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose) has been performed. These all-digital image systems enhance the efficacy of routine examinations.
This department has nine consulting radiologists and 22 technologists. As part of our routine activities, every effort is made to produce an integrated report covering almost all examinations, such as MMG, contrast radiological procedures, CT, MRI, RI, PET, angiography, and IR, mainly transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
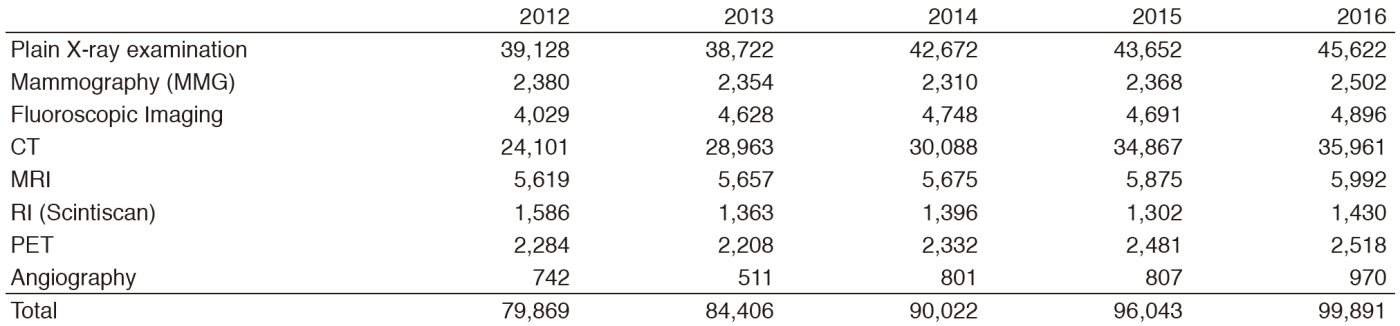
The number of cases examined in 2016 is shown in Table 1. Several conferences are routinely held at our department including pre- and postoperative conferences. Furthermore, our department contributes to decide treatment strategy through the image presentation at the every week tumor board conference (especially, Hepatobiliary-Pancreatic and Head-Neck regions).
Research activities
The Research activities of the Department of Diagnostic Radiology focus on diagnostic imaging and IR. These activities consist of 1) Development of new CT/MRI technologies, and 2) Development of new Nuclear Medicine tracers. Our department also conducts clinical scientific researches as well as basic scientific studies, with the results translated directly into better patient care.
1.Development of new CT/MRI technologies
As a new study using 320 ADCT, we started a research on raw data-based DECT (rDE), and a study on 3D-CTA by test injection method (TI).
rDE is a new and characteristic DECT method of acquiring dual energy data by the ADCT two-rotation method, the new DECT method using the fact that raw data without voltage blur and coordinate shift can be obtained is analyzed more than the conventional DECT is possible. With the basis material analysis (BMA) method which is more precise material separation than the conventional DECT, the new image generation technique which can emphasize the anatomical structure without contrast media was developed. Also, using the virtual monoenergetic images with higher accuracy, the best contrast/noise ratio images were created and the streak artifact was reduced. The comparisons and applications for MAR (Metal artifact reduction) research using ADCT were started.
TI method uses the features of ADCT in temporal resolution and the high time compatibility. The purpose is to get the best timed CTA images for more strategically super-selective intra-arterial chemotherapy in the head and neck. The 3D-CTA with TI showing high contrast-enhancement in the feeding artery and no-contrast-enhancement in the vein around target lesion were generated. As a conventional study using ADCT, along with the study of rDE, the optimization of the voltage in the subtraction image was examined, and images on the high-voltage side and the low-voltage side were obtained. The low-voltage side images showed better contrast in the areas of sinonasal cavities and skullbase than high-voltage side images. In a study using conventional DECT, we examined whether the iodine content can distinguish the thyroid nodules by DECT without contrast enhancement.
In the study using 3T-MRI, in addition to the evaluation of mandibular bone marrow invasion of oral cancer with CS-MPR, in order to evaluate mucosal tumor extension, high-speed MR imaging with oral Valsalva maneuver were tried and images with higher accuracy in the diagnosis of mucosal extension were generated. For a study of bright-blood sequence, the parameter was optimized and diagnostic accuracy increased.
2.Development of new Nuclear Medicine tracers
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) were discovered as a promising gene silencing tool in research and in the clinic, and we previously succeeded with radiolabeled siRNA.
In vivo Biodistribution of siRNAs is important to develop for medical use. Therefore, a novel single photon emitter-labelled siRNA was prepared by using diethylenetriamine-N,N,N'N'',N''-pentaacetic acid (DTPA) and poly(A) polymerase, and subsequently, a real-time analysis of siRNA trafficking was performed by using single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). This study aimed to assess the use of 99mTc-radiolabelled siRNA targeting lacZ to detect lacZ expression in vivo. SiRNA targeting lacZ was radiolabelled with 99mTc by using the bifunctional chelator DTPA, and the labelling efficiency and specific activity were determined. The probe stability in RNaseA was assessed. SPECT imaging was performed in mice overexpressing the lacZ gene in the liver. Radiolabelled siRNA remained highly stable in RNaseA solution at 37℃. In SPECT imaging, significant 99mTc accumulation in the liver has been observed in mice overexpressing the lacZ gene. 99mTc-labelled lacZ siRNA shows s-galactosidase-specific accumulation and appears promising for the visualisation of lacZ expression in vivo. Our labelled siRNA should be deliverable to specific regions overexpressing the target gene.
List of papers published in 2016
Journal
1.Komai Y, Sugimoto M, Gotohda N, Matsubara N, Kobayashi T, Sakai Y, Shiga Y, Saito N. Patient-specific 3-dimensional Printed Kidney Designed for "4D" Surgical Navigation: A Novel Aid to Facilitate Minimally Invasive Off-clamp Partial Nephrectomy in Complex Tumor Cases. Urology, 91:226-233, 2016
2.Goto K, Endo M, Kusumoto M, Yamamoto N, Ohe Y, Shimizu A, Fukuoka M. Bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer: A nested case control study of risk factors for hemoptysis. Cancer Sci, 107:1837-1842, 2016
3.Watanabe Y, Kusumoto M, Yoshida A, Shiraishi K, Suzuki K, Watanabe S, Tsuta K. Cavity Wall Thickness in Solitary Cavitary Lung Adenocarcinomas Is a Prognostic Indicator. Ann Thorac Surg, 102:1863-1871, 2016
4.Bando H, Doi T, Muro K, Yasui H, Nishina T, Yamaguchi K, Takahashi S, Nomura S, Kuno H, Shitara K, Sato A, Ohtsu A. A multicenter phase II study of TAS-102 monotherapy in patients with pre-treated advanced gastric cancer (EPOC1201). Eur J Cancer, 62:46-53, 2016
5.Enokida T, Fujii S, Kuno H, Mukaigawa T, Tahara M, Sakuraba M, Hayashi R. Combined salivary duct carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma suspected of carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma. Pathol Int, 66:460-465, 2016