HOME > Publication & Reports > Annual Report 2016 > Hospital
Department of Ophthalmic Oncology
Shigenobu Suzuki, Yukiko Aihara, Shuichi Sano
Introduction
The Department of Ophthalmic Oncology is one of the rare groups specializing in ocular tumors, especially intraocular tumors. Recently, more than 70% of patients nationwide with retinoblastoma, which is the most frequent intraocular malignancy in childhood, and more than 50% of patients with choroidal melanoma, which is the most frequent primary intraocular malignancy in adults, have been referred to our department.
Our team and what we do
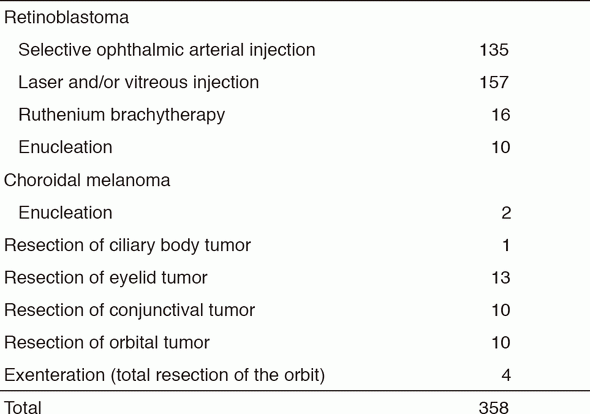
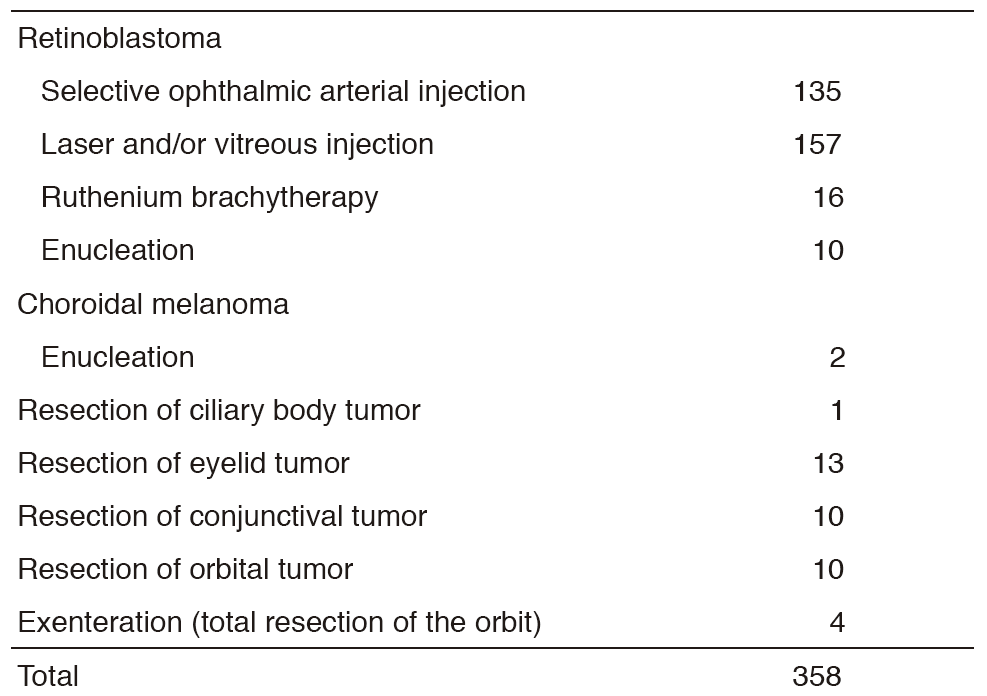
Our outpatient service is open four days a week. Every week, eight operations under general anesthesia are performed in our department. Our treatment strategies for ocular tumors are as follows: (Tables 1, 2)
1.Retinoblastoma
Unless the patient's family has concerns about preserving the affected eye, if the eye has already suffered from complications such as secondary glaucoma or severe hemorrhage, or if extraocular extension of the retinoblastoma is strongly suspected, we can offer the family eye-preserving treatment. Initial systemic chemotherapy and additional local therapies, called "chemoreduction therapy", comprise the main strategy. If the tumor is localized in the peripheral retina, plaque radiotherapy using ruthenium-106 is also available. Transpupillary thermotherapy or cryotherapy is also used in cases with localized small tumors. Patients with extraocular extension, recurrence or metastasis who need intensive systemic chemotherapy are treated with dedicated support from the Department of Pediatric Oncology.
2.Choroidal melanoma
Choroidal melanoma is a rare disease in Asians. Recent reports from Western countries have demonstrated that the prognosis of eye-preserving treatment with plaque radiotherapy is equivalent to that of enucleation (COMS, medium-sized tumor study). For localized tumors up to 5mm thick, ruthenium-106 plaque radiotherapy is the first choice. In Japan, plaque radiotherapy is only available in our institute. Patients with much larger tumors are treated by radiotherapy: CyberKnife Robotic Radiosurgery in our institute or carbon ion therapy in the National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS), the Research Center for Charged Particle Therapy. Choroidal melanomas often metastasize to the liver and this is invariably fatal. Life-long follow-up with liver imaging is routinely conducted for our patients. Patients with liver and systemic metastases are treated by the Department of Dermatologic Oncology.
3.Orbital tumors
Whereas most orbital tumors in childhood are benign, rhabdomyosarcoma is a malignant tumor that requires systemic chemotherapy and radiation after biopsy. The most common orbital tumors in adults include cavernous hemangioma, lacrimal gland tumor, lymphoma, metastatic tumor, and orbital inflammatory disease. Patients with a biopsy-confirmed orbital lymphoma are referred to the Department of Hematology, and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Total resection by orbitotomy, or sometimes orbital exenteration, is used for lacrimal gland tumors.
4.Eyelid tumors
The most common malignant eyelid tumors include basal cell carcinoma, sebaceous carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. They are treated by excisional resection with reconstruction. Radiotherapy using electrons is another strategy. Orbital exenteration is selected in cases of orbital invasion.
5.Conjunctival tumors
Conjunctival malignant tumors are treated by excisional resection with a safety margin combined with cryotherapy at the resection margin. Diffuse conjunctival tumors or tumors with orbital invasion are treated with orbital exenteration.
Research activities
One of the unique techniques in our department is local chemotherapy for retinoblastoma via selective ophthalmic artery infusion using a balloon catheter. This procedure was developed in our hospital from 1987, and has been modified and performed after 2009 in more than 20 countries.
Direct injection of diluted melphalan into the vitreous cavity is performed for retinoblastoma eyes with vitreous seeding. Vitreous seeding can be cured for eyes with vitreous seeds after other treatment modalities, and about 65% of eyes were rescued using this strategy.
The National Registry of Retinoblastoma in Japan was organized in 1975, and more than 3,000 patients are registered. We contribute to this registry as an administrator of personal data and check overlapping. This registry now covers almost all patients in Japan, and provides epidemiological data.
We are now investigating the specific marker or genetic change for eye tumors, especially retinoblastoma, choroidal melanoma, and ciliary body tumors.
We started to establish eye tumor registry and clinical guidelines in cooperation with the Japanese Society of Ocular Oncology.
Ocular adverse events caused by anti-cancer drugs used for systemic disease have been recently recognized, and ocular examinations are included in clinical trials, especially for molecular targeted drugs. Serous retinal detachment (SRD), retinal vein occlusion (RVO), and ocular surface complications are major adverse events caused by kinase inhibitor drugs, stenosis or occlusion of lacrimal drainage systems are common events caused by S-1, and cystoid macular edema (CME) caused by some drugs. We examine and follow these adverse events, with or without additional treatment, to support clinical trials, to contribute to establishing protocols, and to enlighten general ophthalmologists about these events.
Future prospects
We plan to establish the multicenter study group for eye tumors to employ clinical studies, confirm the diagnostic criteria and guidelines, and clarify the carcinogenesis for eye tumors.
List of papers published in 2016
Journal
1.Ophthalmic Oncology Task Force (Gallie BL, Simpson ER, Saakyan S, Amiryan A, Valskiy V, Finger PT, Chin KJ, Semenova E, Seregard S, Fili M, Wilson M, Haik B, Caminal JM, Catala J, Gutierrez C, Pelayes DE, Folgar AM, Jager MJ, Dogrusoz M, Luyten GP, Singh A, Schachat AP, Suzuki S, Aihara Y). Local Recurrence Significantly Increases the Risk of Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. Ophthalmology, 123:86-91, 2016