HOME > Publication & Reports > Annual Report 2016 > Research Institute
RI Research Support Division
Yutaka Yamada, Gen Fujii, Kotaro Suzuki
Introduction
The RI Research Support Division provides advanced technical training and education for researchers in the fields of molecular genetics and radiology. This division is equipped with separate laboratories where registered users can conduct experiments safely with various types of radioisotopes.
Our team and what we do
Our division maintains a joint use facility performing a study support task as one branch of the Research Support Core of the Fundamental Innovative Oncology Core Center (FIOC) since the reorganization within the Natinal Cancer Center Research Institute (NCCRI) in 2014. Our division manages radioisotope (RI) materials and radiation exposure apparatus (Gamma cells with 60-Co and 137-Cs sources), so that the advanced cancer research using these is promoted smoothly. In addition, our division develops radiation management studies so that researchers can use RI resources safely and effectively.
The facility utilizing information
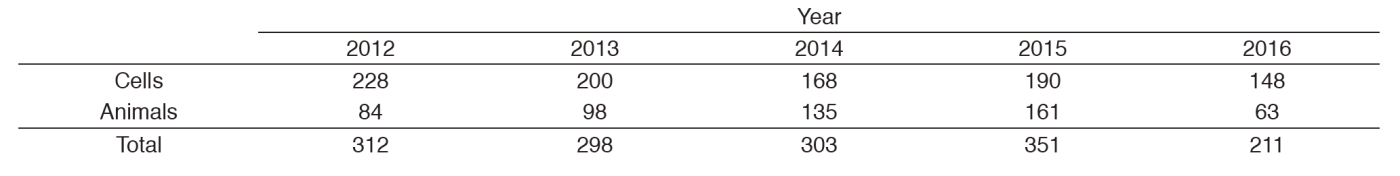
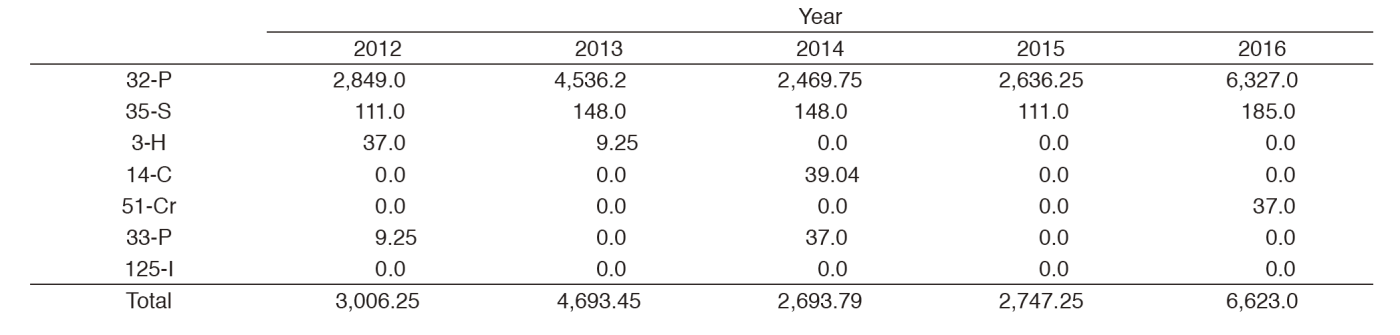
The number of use of the radiation exposure apparatus in 2016 became a total of around 200 times and was the least number for the recent five years (Table 1). 32-P increased the consumption by double in comparison with last year, and 35-S almost remained at the same level, and there was the use of 51-Cr newly (Table 2).
Education
To radiation workers who entered the radiation controlled area, the RI Research Support Division performed education and training about the prevention of radiation hazards.
Future prospects
With the progress of the fluorescence and chemiluminescence technology in the biological science experiment, using RI decreases for the label of nucleotides which has been performed conventionally. On the other hand, in late years an imaging technology in living bodies develops rapidly, and the increase of the usage of a new radionuclide for molecular imaging such as the PET is expected. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is started in the NCC, and it is thought that opportunities to handle neutron-irradiated cells and animals will increase in the basic experiment study. In addition, the radionuclide therapy and the study for the fundamental researches and the clinical applications may be started in the future. The management and education for RI based on a plan for the long-term future in the fields of imaging and radionuclide therapy will be needed.