Annual Report 2017
Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy
Tetsuo Akimoto, Naoki Nakamura, Sadatomo Zenda, Hidenobu Tachibana, Kenji Hotta, Hiromi Baba, Motoki Kumagai
Introduction
The aim of research in the Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy at the National Cancer Center Hospital East (NCCHE) is to study and develop innovative treatment techniques and pilot a clinical trial for proton beam therapy (PBT). Medical physicists mainly perform the development and verification of the systems for beam irradiation, a dose calculation system, dose measurement, and imaging of PBT. Radiation oncologists mainly perform studies on the clinical trials, efficacy, and side-effects of PBT.
Our team and what we do
At present, the staff of the Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy consists of seven consultant physicians (radiation oncologists), six radiation technologists, four medical physicists, one nurse, and one clerk. We have more than 300 new patients for PBT every year, and quality assurances of PBT are performed by medical physicists and radiation technologists, and a conference on verification of treatment planning is held every morning in addition to a weekly work conference regarding research activities. PBT is routinely based on three-dimensional radiation therapy planning and PBT using RT-dedicated multi-detector-row helical computed tomography (CT) scanning in order to confirm a precise radiation dose to the targeted tumors. Respiratory-gating has been applied especially in radiotherapeutic management for patients with lung, esophagus, and liver cancers.
Our division is responsible for PBT that is composed of seven operating staff members and one technician for fabricating the compensator and aperture; they are sent from manufacturing companies and work in collaboration with other staff members of our division. PBT consists of two treatment rooms, both of which are routinely used for rotational gantry treatment. Our division ensures quality assurance and regular maintenance of the PBT machines for precise dose delivery and safe treatment.
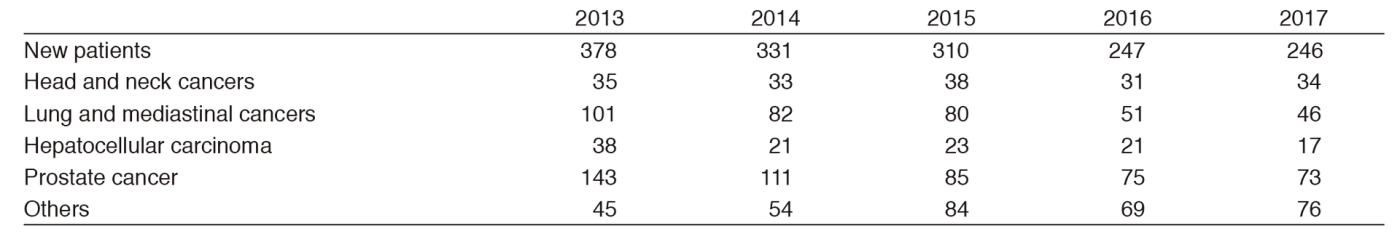
Table 1. Number of patients treated with PBT during 2013-2017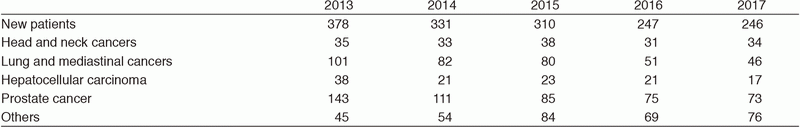
Research activities
1) PBT as a nonsurgical approach to mucosal melanoma of the head and neck: a pilot study
2) Phase II study of PBT combined with chemotherapy for inoperable non-small cell lung cancer
3) Phase I/II study of dose escalated PBT combined with chemotherapy for esophageal cancer
4) Non-randomized prospective comparative study between surgical resection and proton beam therapy for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma
5) Establishment of feasibility and effectiveness of line scanning for localized prostate cancer
6) Proton dose distribution measurements using a MOSFET detector with a simple dose-weighted correction method for LET effects
7) Radiobiological evaluation of cellular response to PBT
8) Radiobiological evaluation of combined effect of chemotherapeutic agents on enhancement of PBT
9) Standardization of methods of PBT and quality assurance of PBT among Japanese proton beam facilities
10) Establishment of infrastructure for multi-
institutional study of PBT for various cancers. Technical development of intensity modulated proton beam therapy (IMPT)
11) In silico comparison of dose distribution between IMRT and IMPT for locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Clinical trials
The following in-house and multi-institutional clinical trials are under way.
1) Phase II study of PBT for malignant melanoma of nasal cavity
2) Phase II study of PBT combined with chemotherapy for inoperable non-small cell lung cancer
3) Phase I/II study of dose escalated study of PBT combined with chemotherapy for esophageal cancer
4) Phase I/II study of line scanning for localized prostate cancer
5) Non-randomized prospective comparative study between surgical resection and proton beam therapy for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma
Education
We established an education and training system for residents and junior radiation oncologists through clinical conferences and lectures on radiation oncology, physics, and radiation biology. In addition, a training course regarding quality assurance of radiation therapy including PBT has been regularly held for medical physicists and radiological technologists.
Future prospects
We are now aiming at the establishment of a system that can provide high-quality and safe PBT. In addition, we would like to promote the research and development of innovative technologies regarding PBT, radiation biology, and medical physics.
List of papers published in January 2017 - March 2018
Journal
1. Kawai D, Takahashi R, Kamima T, Baba H, Yamamoto T, Kubo Y, Ishibashi S, Higuchi Y, Tani K, Mizuno N, Jinno S, Tachibana H. Variation of the prescription dose using the analytical anisotropic algorithm in lung stereotactic body radiation therapy. Phys Med, 38:98-104, 2017
2. Moriya S, Tachibana H, Hotta K, Nakamura N, Sakae T, Akimoto T. Feasibility of dynamic adaptive passive scattering proton therapy with computed tomography image guidance in the lung. Medical physics, 44:4474-4481, 2017
3. Hojo H, Dohmae T, Hotta K, Kohno R, Motegi A, Yagishita A, Makinoshima H, Tsuchihara K, Akimoto T. Difference in the relative biological effectiveness and DNA damage repair processes in response to proton beam therapy according to the positions of the spread out Bragg peak. Radiat Oncol, 12:111, 2017
4. Uchida Y, Tachibana H, Kamei Y, Kashihara K. Effectiveness of a simple and real-time baseline shift monitoring system during stereotactic body radiation therapy of lung tumors. Phys Med, 43:100-106, 2017
5. Kurosawa T, Tachibana H, Moriya S, Miyakawa S, Nishio T, Sato M. Usefulness of a new online patient-specific quality assurance system for respiratory-gated radiotherapy. Phys Med, 43:63-72, 2017
6. Sugawara Y, Tachibana H, Kadoya N, Kitamura N, Sawant A, Jingu K. Prognostic factors associated with the accuracy of deformable image registration in lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. Med Dosim, 42:326-333, 2017
7. Nishiyama S, Ishibashi S, Takahashi R, Tachibana H. Independent dose verification for brain stereotactic radiotherapy using different add-on micro multi-leaf collimators. Radiol Phys Technol, 10:286-293, 2017
8. Nakamura N, Zenda S, Tahara M, Okano S, Hayashi R, Hojo H, Hotta K, Kito S, Motegi A, Arahira S, Tachibana H, Akimoto T. Proton beam therapy for olfactory neuroblastoma. Radiother Oncol, 122:368-372, 2017
9. Moriya S, Tachibana H, Kitamura N, Sawant A, Sato M. Dose warping performance in deformable image registration in lung. Phys Med, 37:16-23, 2017
10. Demizu Y, Mizumoto M, Onoe T, Nakamura N, Kikuchi Y, Shibata T, Okimoto T, Sakurai H, Akimoto T, Ono K, Daimon T, Murayama S. Proton beam therapy for bone sarcomas of the skull base and spine: A retrospective nationwide multicenter study in Japan. Cancer Sci, 108:972-977, 2017
