Annual Report 2019
Section of Knowledge Integration
Shinji Kohsaka, Risa Miyagawa, Katsuyuki Ikarashi, Taro Shibata, Yasushi Goto, Kazuya Tsuchihara
Introduction
- Development of Cancer Knowledge Data Base
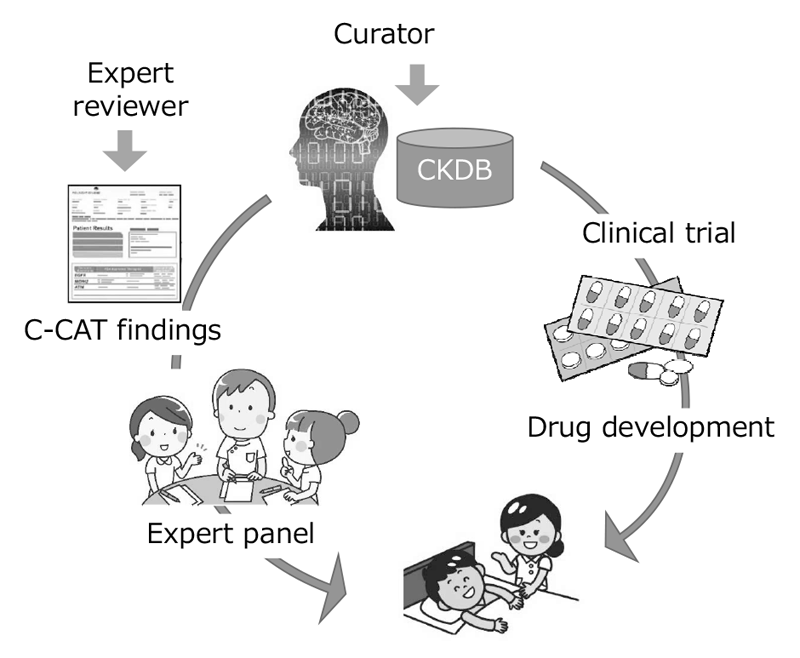
CKDB (Cancer Knowledge Data Base) was developed to improve the quality of cancer genome testing. Moreover, a curator team consisted of about 25 clinical oncologists and bioinfomaticians was organized to maintain the system, updating data of clinical trials, medicines and maker evidence monthly.
The Team and What We Do
We provided expert panel C-CAT findings, a report summary of clinical trials, medicines and maker evidence to annotate clinical significance to variants found by cancer panel testing performed by clinical laboratories. We also established a management system to control the quality of C-CAT findings by standardizing the process of the review by expert reviewers, who are equivalent to M.D. or Ph.D. About 3,000 C-CAT findings were provided to expert panels of core hospitals between June 2019 and March 2020.
Research activities
CKDB was developed by collecting, standardizing and integrating the information of maker evidence, anti-cancer therapies and clinical trials. Using the CKDB, we constructed a system to generate C-CAT findings. CKDB-portal was also developed to search, query and curate the knowledge stored in CKDB.
Education
Monthly curator meetings were held to educate the curators and maintain the quality of CKDB curation. Monthly expert reviewer meetings were held to educate the expert reviewers and standardize the review process of C-CAT findings.
Future prospects
C-CAT findings support the expert panel with information on the newest evidence, anti-cancer therapies and clinical trials, and, as a result, the genome medicine will be uniformly and efficiently promoted. Furthermore, promotion of clinical trials will activate new drug development in Japan, lead to the discovery of evidence and contribute to great progress in cancer medicine (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Development of CKDB to improve the quality of genome medicine