Annual Report 2019
Division of Cancer Biology
Hirofumi Arakawa, Yasuyuki Nakamura, Naoki Ikari, Takahiro Shibata, Yoko Sagami, Katsuko Honjo, Hidefumi Suzuki
Research activities
1. Mieap-regulated mitochondrial quality control
Mieap controls mitochondrial quality via two distinct novel mechanisms. One of the mechanisms has been designated MALM for Mieap-induced accumulation of lysosome-like organelles within mitochondria (PLoS ONE 6: e16054, 2011). In this mechanism, Mieap induces the accumulation of intramitochondrial lysosomal proteins in order to eliminate oxidized mitochondrial proteins in response to mitochondrial damage. This leads to a decrease in reactive oxygen species generation and an increase in mitochondrial ATP synthesis activity, implying MALM plays a role in repairing unhealthy mitochondria.
BNIP3 and NIX, mitochondrial outer membrane proteins, are two Mieap-interacting proteins that mediate the translocation of lysosomal proteins from cytosol into mitochondria during MALM by forming an unknown pore in the mitochondrial double membrane (PLoS ONE 7: e30767, 2012). 14-3-3γ mediates the degradation of oxidized mitochondrial proteins within mitochondria during MALM (Scientific Reports 2: 379, 2012).
Alternatively, the other mechanism has been designated MIV for Mieap-induced vacuole (PLoS ONE 6: e16060, 2011). When MALM is inhibited, Mieap induces a vacuole-like structure, MIV. The MIV engulfs the damaged mitochondria and accumulates lysosomes, leading to the degradation of unhealthy mitochondria. MIV likely represents a novel mechanism for mitochondrial autophagy, also called “mitophagy”. Therefore, Mieap controls mitochondrial quality by repairing or eliminating unhealthy mitochondria via MALM or MIV generation, respectively.
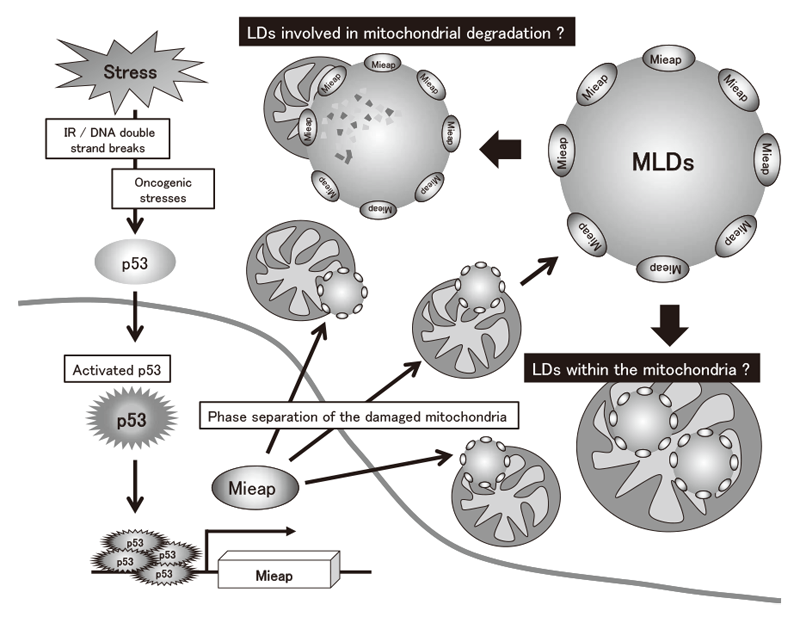
This year, we found that Mieap forms liquid droplets (Mieap liquid droplets: MLDs) in the mitochondria by phase-separating mitochondrial constituents (Figure 1). Liquid droplets (LDs) are protein condensates that function as membrane-less organelles, which compartmentalize essential biochemical reactions in the cell, including transcriptional regulation, metabolism, signal transduction, and mitosis. LDs rapidly appear and disappear in response to various cellular stresses and/or subcellular conditions, exhibiting spatiotemporal dynamic properties. We speculate that MLDs function as membrane-less organelles that compartmentalize enzymatic reactions in the mitochondria, or that degrade unhealthy mitochondria. Thus, MLDs play a critical role in tumor suppression by phase-separating the damaged mitochondrial materials to maintain the mitochondrial integrity. Our research will elicit a paradigm shift in the concept for MQC and tumor suppression, which will enable us to comprehend the complete mechanism underlying p53 tumor suppression.
2. Mieap-regulated mitochondrial quality control is frequently inactivated in human cancer
The accumulation of unhealthy mitochondria results in mitochondrial dysfunction, which has been implicated in aging, degenerative diseases and cancer. The Mieap-regulated mitochondrial quality control (MQC) was found to be frequently inactivated by p53 mutations or Mieap/BNIP3 promoter methylation in more than 70% of primary cancer tissues of colorectal cancer patients, leading to accumulation of unhealthy mitochondria and a high level of mitochondria reactive oxygen species generation (ROS) (Oncogenesis 5: e181, 2016). The Mieap-regulated MQC was also inactivated in 26% of primary cancer tissues of breast cancer patients (Cancer Science 109: 3910-3920, 2018).
3. Mieap-deficient cancer animal model
To clarify the in vivo role of the Mieap-regulated MQC in tumorignenesis, Mieap knockout mice were generated in the Division. Using the Mieap knockout mice, Mieap-deficient ApcMin/+ mice were also generated and analyzed in order to elucidate the role of Mieap in colorectal cancer tumorigenesis (Scientific Reports 5: 12472, 2015).
Interestingly, the Mieap-deficient ApcMin/+ mice exhibited remarkably reduced lifespans compared with those of ApcMin/+ mice. Furthermore, a substantial increase in the number and size of intestinal polyps was found in the Mieap-deficient ApcMin/+ mice. Histopathologically, intestinal tumors in the Mieap-deficient ApcMin/+ mice clearly exhibited advanced grades of adenoma and adenocarcinomas. Unhealthy mitochondria dramatically accumulated in the tumor cells and generated a high level of ROS in the Mieap-deficient ApcMin/+ mice.
We further obtained the same results from Mieap-deficient gastric cancer model mice. These results suggest that the Mieap-regulated MQC pathway has a critical role in the suppression of intestinal tumors in vivo.
Future prospects
Analyses of cancer cell lines, clinical cancer tissues, and cancer-mouse models enable us to understand the actual role of the Mieap-regulated mitochondrial quality control in human cancer initiation, progression, invasion and metastasis. Finally, we will be able to establish a solid foundation for development of new strategies for cancer prevention, diagnosis, and therapy in the future.
List of papers published in 2019
Journal
1. Tamanaha-Nakasone A, Uehara K, Tanabe Y, Ishikawa H, Yamakawa N, Toyoda Z, Kurima K, Kina S, Tsuneki M, Okubo Y, Yamaguchi S, Utsumi D, Takahashi K, Arakawa H, Arasaki A, Kinjo T. K1 gene transformation activities in AIDS-related and classic type Kaposi's sarcoma: Correlation with clinical presentation. Sci Rep, 9:6416, 2019
