Annual Report 2019
Central Radioisotope Division
Masamichi Ishiai, Gen Fujii, Hiroshi Tanooka, Junko Suzuki, Hideyuki Watanuma
Introduction
The Central Radioisotope Division is a joint usage facility composed of the Research Support Core of the Fundamental Innovate Oncology Core (FIOC) of the National Cancer Center (NCC) Research Institute. We provide advanced technical training and education for researchers in the NCC.
The Team and What We Do
Our division manages radioisotope (RI) materials, gamma-ray irradiators (Gammacell 220 with Co-60 source, and Gammacell 40 Exactor with Cs-137 source), and radiation-related equipment, to promote advanced cancer research smoothly. In addition, our division conducts radiation management studies so that researchers can use RI resources safely and effectively.
Research activities
We have focused on the molecular mechanisms of DNA damage responses and/or DNA repair pathways after irradiation, and cancer chemoprevention.
The facility utilization information
Comparing the pre (2016) and post (2018 and 2019) relocation periods of the Research Institute (2017), the usage of gamma-ray irradiator (Table 1) recovered to almost the same level. Especially, the number of mice (animal in the table) experiments showed steady recovery. While the used amount of RI (Table 2) did not recover to pre-relocation (2016) levels, the reason was possibly the stimulation of the transition in the style of experiments (i.e. transition from RI to non-RI experiments).
Table 1. Usage times of gamma-ray irradiator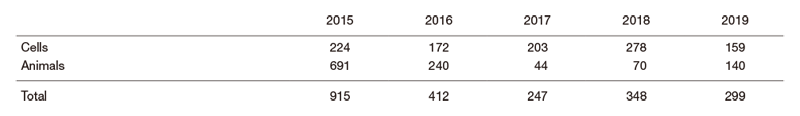
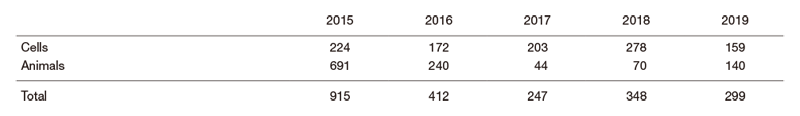
Table 2. Used amounts of radioisotopes (MBq)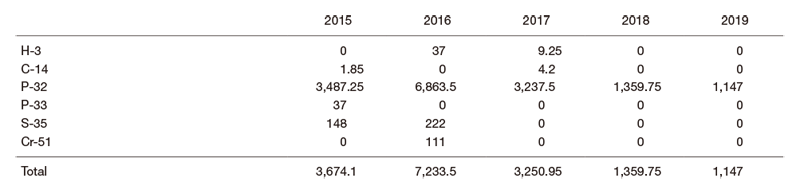
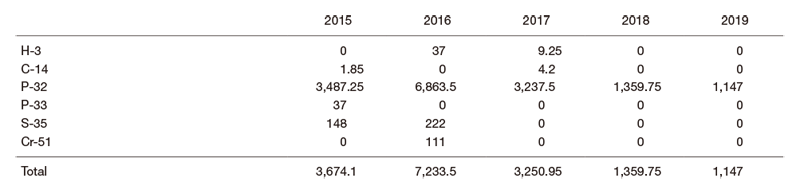
Future prospects
Recently, live imaging technology for cells and/or animals has been developing, and the usage of radionuclides for molecular imaging such as positron emission tomography (PET) has increased. In the NCC, boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) has started, and this caused the increased in opportunities to handle neutron-irradiated cells in our division. In addition, basic and/or clinical research intended for radionuclide therapy will start. The management, equipment, and education necessary for these new-age radiation technologies for cancer research will be urgently needed in our division.
List of papers published in 2019
Journal
1. Adachi S, Hamoya T, Fujii G, Narita T, Komiya M, Miyamoto S, Kurokawa Y, Takahashi M, Takayama T, Ishikawa H, Tashiro K, Mutoh M. Theracurmin inhibits intestinal polyp development in Apc-mutant mice by inhibiting inflammation-related factors. Cancer Sci, 111:1367-1374, 2020
2. Kurokawa Y, Fujii G, Tomono S, Miyamoto S, Hamoya T, Takahashi M, Narita T, Komiya M, Kobayashi M, Higami Y, Mutoh M. The Radical Scavenger NZ-419 Suppresses Intestinal Polyp Development in Apc-Mutant Mice. J Clin Med, 9:pii: E270. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010270, 2020
3. Miyamoto S, Narita T, Komiya M, Fujii G, Hamoya T, Nakanishi R, Tamura S, Kurokawa Y, Takahashi M, Mutoh M. Novel screening system revealed that intracellular cholesterol trafficking can be a good target for colon cancer prevention. Sci Rep, 9:6192, 2019
4. Mawaribuchi S, Onuma Y, Aiki Y, Kuriyama Y, Mutoh M, Fujii G, Ito Y. The rBC2LCN-positive subpopulation of PC-3 cells exhibits cancer stem-like properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 515:176-182, 2019
5. Takahashi M, Fujii G, Hamoya T, Kurokawa Y, Matsuzawa Y, Miki K, Komiya M, Narita T, Mutoh M. Activation of NF-E2 p45-related factor-2 transcription and inhibition of intestinal tumor development by AHCC, a standardized extract of cultured Lentinula edodes mycelia. J Clin Biochem Nutr, 65:203-208, 2019
6. Tamura S, Narita T, Fujii G, Miyamoto S, Hamoya T, Kurokawa Y, Takahashi M, Miki K, Matsuzawa Y, Komiya M, Terasaki M, Yano T, Mutoh M. Inhibition of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity enhances fucoxanthinol-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Genes Environ, 41:1 doi: 10.1186/s41021-018-0116-1, 2019
7. Fujimoto K, Ohta T, Yamaguchi H, Tung NH, Fujii G, Mutoh M, Uto T, Shoyama Y. Suppression of polyp formation by saffron extract in ApcMin/+ mice. Phcog Res, 11:96-101. DOI: 10.4103/pr.pr_152_18, 2019
