Annual Report 2021
Central Radioisotope Division
Masamichi Ishiai, Gen Fujii, Shoji Imamichi, Hiroshi Tanooka, Mitsuko Masutani, Makoto Ihara, Takae Onodera, Kaima Tsukada, Takahiro Hamoya, Takahisa Hirai, Hideyuki Watanuma, Rikiya Imamura
Introduction
The Central Radioisotope Division is a joint usage facility composed of the Research Support Core of the Fundamental Innovate Oncology Core (FIOC) of the National Cancer Center (NCC) Research Institute. We provide advanced technical training and education for researchers in the NCC. We also support and advise on radiation-related biological research.
The Team and What We Do
Our division manages radioisotope (RI) materials, gamma-ray irradiators (Gammacell 220 with Co-60 source and Gammacell 40 Exactor with Cs-137 source), and radiation-related equipment to promote advanced cancer research in a smooth manner. Our division also conducts radiation management studies so that researchers can use RI resources safely and effectively.
Research activities
We have focused on the study of molecular mechanisms of cellular responses such as DNA damage signaling, DNA repair, and apoptosis pathways after DNA damage, including by irradiation.
Through collaboration with the Radiation Oncology at the NCC Hospital and industry, we conducted preclinical research as well as basic and translational studies of the accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) system introduced in the NCC and research on boron carrier drugs.
We have also investigated the molecular mechanisms of chemical carcinogenesis and cancer chemoprevention.
The research topics were presented at international and domestic academic conferences and published as treatises.
Facility utilization information
The usage frequency of gamma-ray irradiators and the used amounts of RI for the past five years are shown in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. While the frequency of radiation-related experiments decreased in the relocation period of the Research Institute (2017), they have been steadily recovering.
Table 1. Number of times gamma-ray irradiators were used
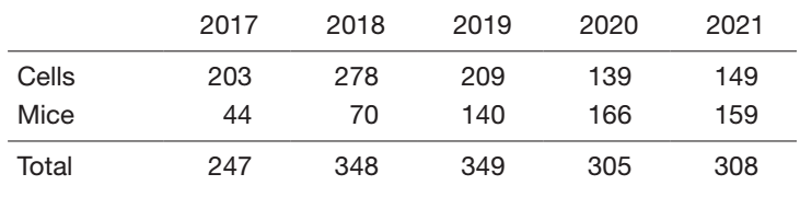
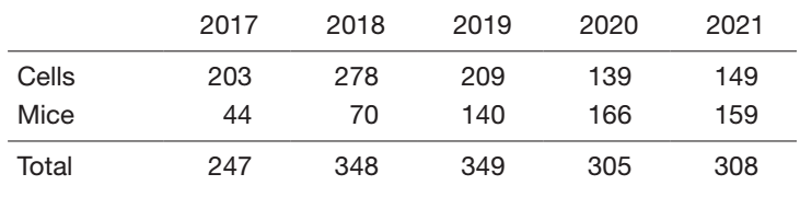
Table 2. Used amounts of radioisotopes (MBq)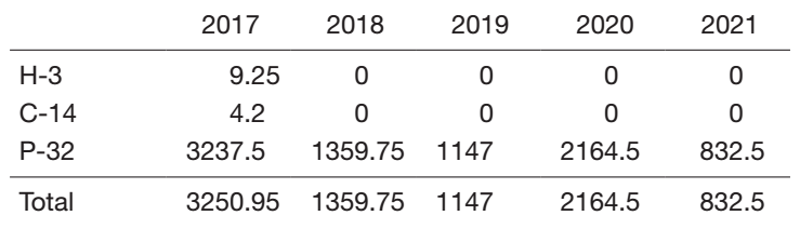

Education
We provide an annual course for education and training in radiation biology, handling of RI, and operation of gamma-ray irradiators.
Two graduate school students were trained in our division, and one got a Ph.D.
Future Prospects
A clinical trial for cancer patients using BNCT has been initiated in the NCC Hospital, so opportunities to handle neutron-irradiated cells have increased in our division. In addition, there are plans to start basic and clinical research on radionuclide therapy. The management, equipment, and education required for these new-generation radiation technologies for cancer research will be urgently needed in our division.
List of papers published in 2021
Journal
1. Imamichi S, Chen L, Ito T, Tong Y, Onodera T, Sasaki Y, Nakamura S, Mauri P, Sanada Y, Igaki H, Murakami Y, Suzuki M, Itami J, Masunaga S, Masutani M. Extracellular Release of HMGB1 as an Early Potential Biomarker for the Therapeutic Response in a Xenograft Model of Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Biology, 11:2022
2. Narita T, Tsunematsu Y, Miyoshi N, Komiya M, Hamoya T, Fujii G, Yoshikawa Y, Sato M, Kawanishi M, Sugimura H, Iwashita Y, Totsuka Y, Terasaki M, Watanabe K, Wakabayashi K, Mutoh M. Induction of DNA Damage in Mouse Colorectum by Administration of Colibactin-producing Escherichia coli, Isolated from a Patient With Colorectal Cancer. In vivo (Athens, Greece), 36:628-634, 2022
3. Tanooka H. Radiation cancer risk at different dose rates: new dose-rate effectiveness factors derived from revised A-bomb radiation dosimetry data and non-tumor doses. Journal of radiation research, 63:1-7, 2022
4. Chen L, Imamichi S, Tong Y, Sasaki Y, Onodera T, Nakamura S, Igaki H, Itami J, Masutani M. A Combination of GM-CSF and Released Factors from Gamma-Irradiated Tumor Cells Enhances the Differentiation of Macrophages from Bone Marrow Cells and Their Antigen-Presenting Function and Polarization to Type 1. Medicines (Basel, Switzerland), 8:2021
5. Nakamura S, Igaki H, Ito M, Imamichi S, Kashihara T, Okamoto H, Nishioka S, Iijima K, Chiba T, Nakayama H, Takemori M, Abe Y, Kaneda T, Takahashi K, Inaba K, Okuma K, Murakami N, Nakayama Y, Masutani M, Nishio T, Itami J. Neutron flux evaluation model provided in the accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy system employing a solid-state lithium target. Scientific reports, 11:8090, 2021
6. Oishi T, Sasaki Y, Tong Y, Chen L, Onodera T, Iwasa S, Udo E, Furusato B, Fujimori H, Imamichi S, Honda T, Bessho T, Fukuoka J, Ashizawa K, Yanagihara K, Nakao K, Yamada Y, Hiraoka N, Masutani M. A newly established monoclonal antibody against ERCC1 detects major isoforms of ERCC1 in gastric cancer. Global health & medicine, 3:226-235, 2021
7. Yoshioka KI, Kusumoto-Matsuo R, Matsuno Y, Ishiai M. Genomic Instability and Cancer Risk Associated with Erroneous DNA Repair. International journal of molecular sciences, 22:2021
8. Takahashi M, Hamoya T, Narita T, Fujii G, Totsuka Y, Hagio M, Tashiro K, Komiya M, Mutoh M. Complex Modulating Effects of Dietary Calcium Intake on Obese Mice. In vivo (Athens, Greece), 35:2107-2114, 2021
9. Ishiai M. Regulation of the Fanconi Anemia DNA Repair Pathway by Phosphorylation and Monoubiquitination. Genes, 12:2021
